blog: hpc-2025-distributed-system
blog: hpc-2025-heterogeneous-system
blog: hpc-2025-program-smp-platform
7.1 KiB
title, date, tags
| title | date | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Performance Computing 25 SP Distributed System | 2025-05-10T00:31:39.3109950+08:00 |
|
The motivation of distributed system is resource sharing.
Definition of a Distributed System
- A collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single coherent system.
- A system in which hardware and software components located at networked computers communicated and coordinate their actions on by message passing.
Important aspects:
- Components are autonomous.
- Virtually single systems as transparency.
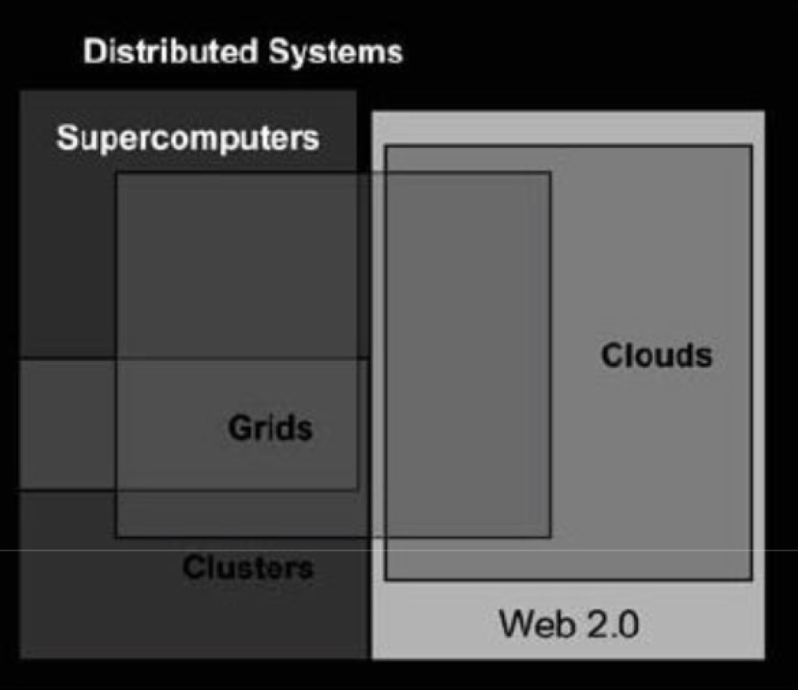
Kinds of Systems
Clustering:
A cluster is a group of independent resources that are interconnected and work as a single system.
A general prerequisite of hardware clustering is that its component systems have reasonably identical hardware and operating system to provide similar performance levels when one failed component is to be replaced by another.
Peer-to-Peer Network:
P2P system are quite popular for file sharing, content distribution and Internet telephony.
Grid Computing:
A computing grid (or computational grid ) provides a platform in which computing resources are organized into one or more logical pools.
Cloud Computing:
Enables clients to outsource their software usage, data storage and even the computing infrastructure to remote data centers.
Fog Computing:
Fog computing focuses processing efforts at the local area network end of the chain.
Edge Computing:
Edge computing takes localized processing a bit farther, push these efforts closer to the data sources.
Near Resources Computing:
While CPU becomes powerful, I/O devices too. So offload CPU for domain-specific computing.
Features of Distributed System
Transparency:
- Access transparency.
- Location transparency.
- Migration transparency.
- Relocation transparency.
- Replication transparency.
- Concurrency transparency.
- Failure transparency.
Openness:
- Open distributed systems: offer services according to standard rules that describe the syntax and semantics of those services.
- Services are specified through interfaces.
Scalability:
Size scalability: more users and more resources.
- Centralized services: a single server for all users.
- Centralized data: a single on-line telephone book.
- Centralized algorithms: doing routing based on completed information.
Common Problems is Distributed Systems
- Leader Election
- Mutual Exclusion
- Time Synchronization
- Global State
- Multicasting
- Replica Management
Time in Distributed Systems
Atomic clocks: modern timekeepers use atomic clocks as a de facto primary standard of time.
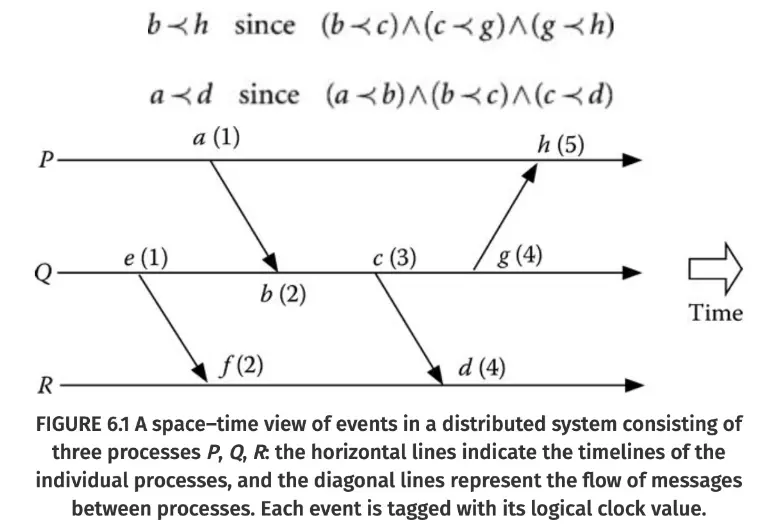
Happened Before Relationship:
Three basic rules about the causal ordering of events, and they collectively define the happened before a.k.a the causally ordered before relationship.
- Rule 1: Let each process have a physical clock whose value is monotonically increasing.
- Rule 2: If a is the event of sending a message by process P, and b is the event of receiving the same message by another process Q, so the a < b.
- Rule 3: a < b and b < c can lead to a < c.
The space time diagrams show such relationship:
Logical Clocks:
A logical clock is an event counter that respects causal ordering.
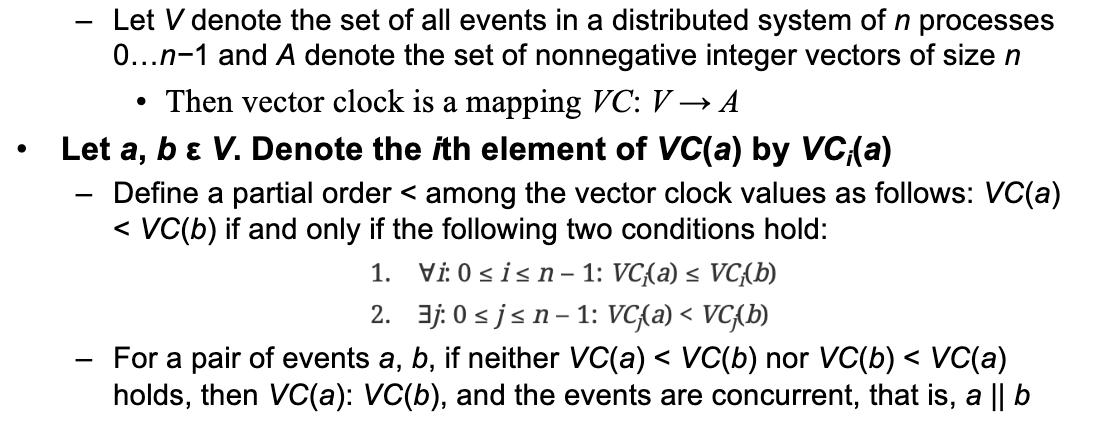
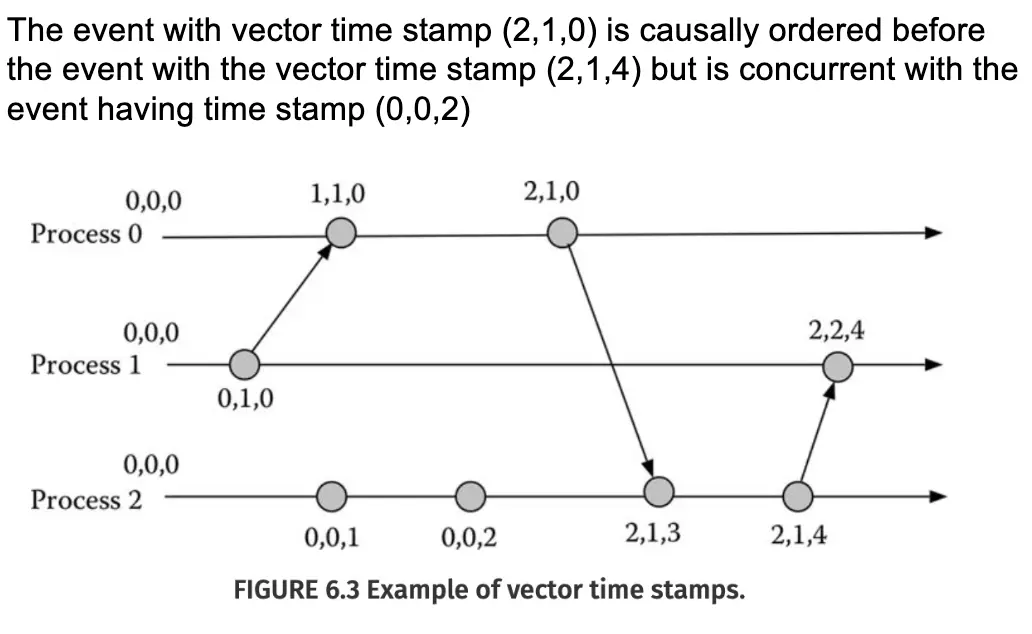
Vector Clocks:
The primary goal of vector clocks is to detect causality, which is the major weakness of logical clocks.
Synchronization Classification:
Types of synchronization:
- External synchronization
- Internal synchronization
- Phase synchronization
Types of clocks:
- Unbounded
- Bounded
Unbounded clocks are not realistic but are easier to deal with in the design of algorithms. Real clocks are always bounded.
External Synchronization:
To maintain the reading of each clock as close to the UTC as possible.
The NTP is an external synchronization protocol.
Internal Synchronization:
To keep the readings of a system of autonomous clocks closely synchronized with one another, despite the failure or malfunction of one or more clocks.
Of course external synchronization implies internal synchronization.
Phase Synchronization:
Many distributed computations run in phases: in a given phase all processes execute some actions which are followed by the next phase.
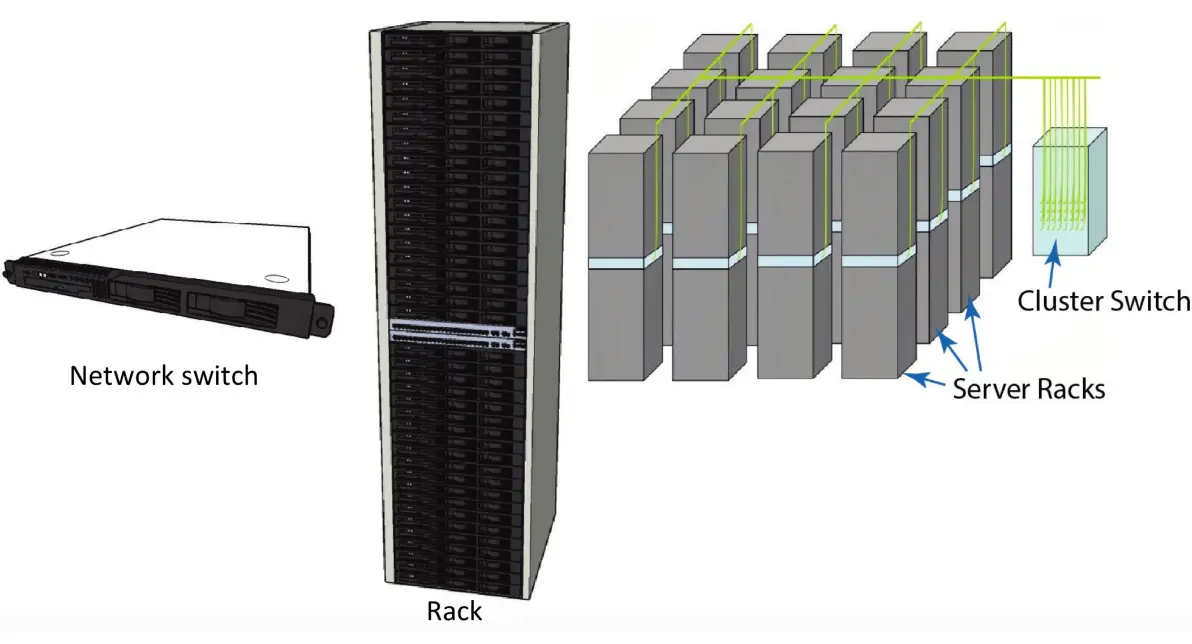
Data Center Organization
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components.
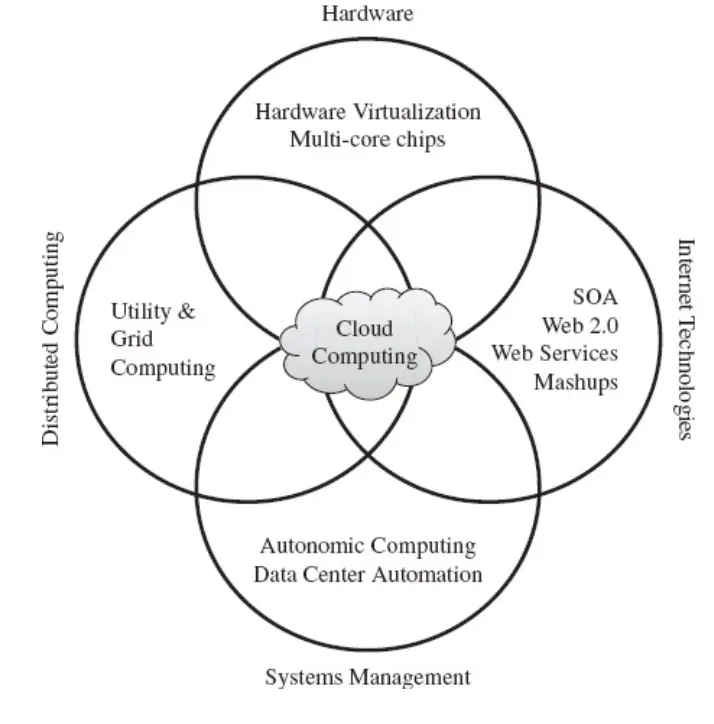
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a specialized form of distributed computing that introduces utilization models for remotely provisioning scalable and measured resources.
NIST definition:
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.
Cloud Characteristics:
- On-demand Usage
- Ubiquitous Access
- Multitenancy
- Elasticity
- Measure Usage
- Resiliency
Cloud Delivery Models:
A cloud service delivery model represents a specific pre-packaged combination of IT resources offered by a cloud provider.
- Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS - Platform as a a Service
PaaS - Software as a Service
SaaS
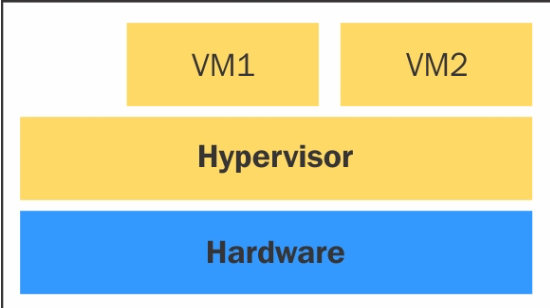
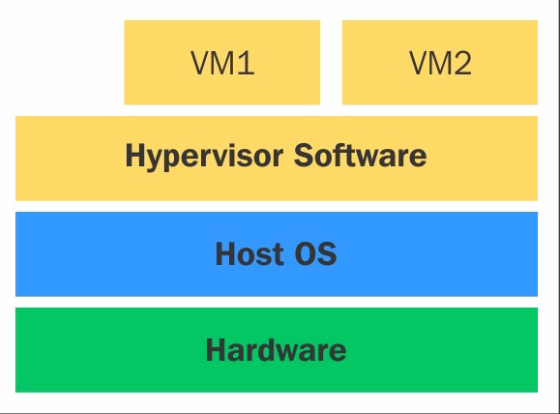
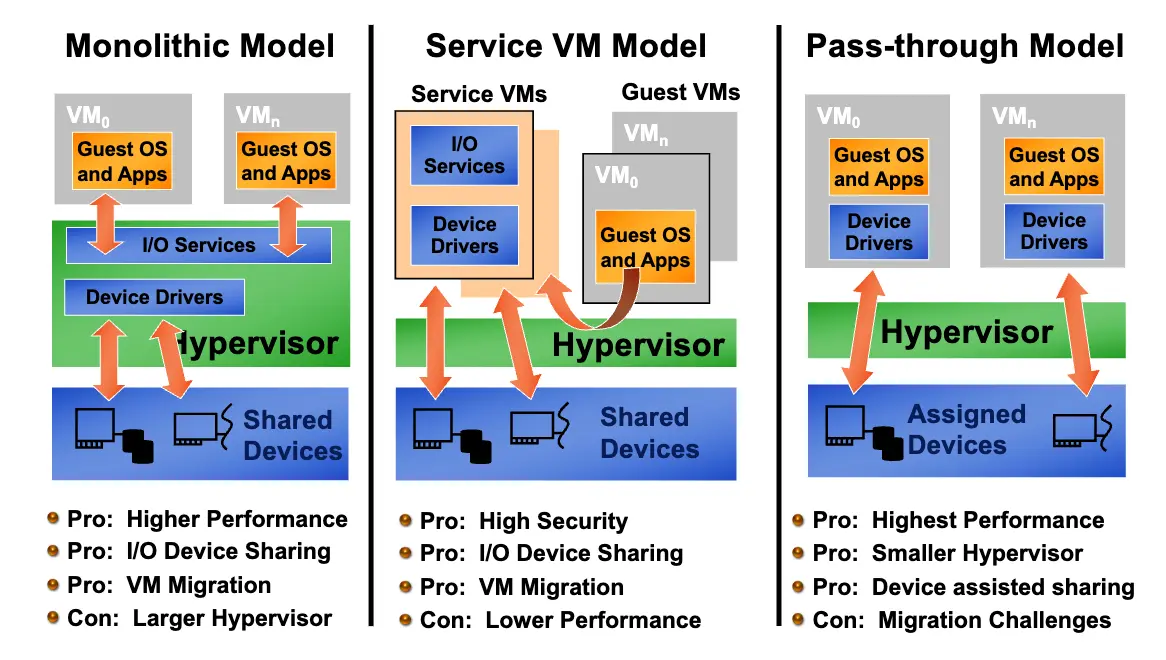
Hypervisor:
Type 1 hypervisor:
Type 2 hypervisor:
CPU Virtualization:
Inter VT-X and AMD SVM:
- Introduce virtualization technology processors with an extra instruction set called Virtual Machine Extensions or VMX.
- Add additional operating model for host and guest.
- Support for swapping state between guest and host.
- Support for hiding privileged state.
Big Data Processing
MapReduce Programming Model
MapReduce is based on a very simple idea for parallel processing of data-intensive applications supporting arbitrarily divisible load sharing.
The so-called same process multiple data (SPMD) paradigm.
MapReduce Logical Data Flow:
The input data and output data of both the Map and reduce functions has a particular structure.
Sending computation toward data rather than sending data toward computation.
Resilient Distributed Dataset
An RDD is a read-only partitioned collection of records.